kelly0303
- 573
- 33
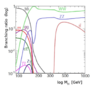
Hello! In the (famous) plot I attached we have the branches ratios for the Higgs decay for different Higgs masses. I am sure that sitting down and doing the Feynman diagram calculation (to 1 or 2 next to leading order?) I will get these curves. But I am a bit confused about the physics intuition behind the decay to W and Z. The coupling between Z and Higgs is bigger than the coupling between W and Higgs (by a factor of ##\frac{1}{(cos{\theta_w})^2}##). Yet the branching ratio for Higgs to WW is almost double that Higgs to ZZ for a wide range of energies. Of course the mass of the Z is higher so the phase space is smaller in this case, compared to W, but I wouldn't expect that a 10GeV difference to create such a big effect on the branching ratio, especially at big Higgs masses where a 10GeV difference should be almost insignificant. Is there a physical intuition as to why is this happening or it's just math and renormalization group stuff, without an actual deep physical meaning? What I mean by this is: could someone, knowing all the parameters involved, but without actually calculating the Feynman diagrams, predict that the branching ratio to W will be bigger than to Z? Thank you!