SUMMARY
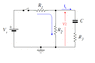
The discussion centers on the behavior of current through a capacitor when a switch is opened in a circuit containing resistors R1, R2, and R3. It is established that when the switch is closed, the capacitor charges to the supply voltage of 5.5V, and the current through the capacitor is zero at steady state. Upon opening the switch, the capacitor begins to discharge, and the current can be calculated using the formula Ic = Vo/(R2 + R3), where Vo is the voltage across R2. The voltage at the open terminals of the capacitor is not zero, as a potential difference exists even without current flow.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of capacitor charging and discharging principles
- Familiarity with Ohm's Law (V=IR)
- Knowledge of voltage dividers in electrical circuits
- Basic concepts of series and parallel resistor configurations
NEXT STEPS
- Study the transient response of RC circuits during charging and discharging
- Learn about the exponential decay of current in capacitive circuits
- Explore the use of voltage dividers in more complex circuits
- Investigate the impact of different resistor values on capacitor discharge rates
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and anyone interested in understanding capacitor behavior in RC circuits.