SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on using De Moivre's theorem to express powers in polar form. The user demonstrates the application of the theorem by calculating P as 4*[cos(30°) + i*sin(30°)] and subsequently finding P²/10 as 1.6*[cos(60°) + i*sin(60°)]. It is clarified that there is no need to divide the angle of 60° by 10, maintaining the final argument as 60°.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of De Moivre's theorem
- Familiarity with polar coordinates
- Basic knowledge of complex numbers
- Trigonometric functions (sine and cosine)
NEXT STEPS
- Study the applications of De Moivre's theorem in complex number calculations
- Explore polar form representation of complex numbers
- Learn about the properties of trigonometric functions in polar coordinates
- Investigate advanced topics in complex analysis
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in mathematics, particularly those studying complex numbers and trigonometry, as well as educators teaching these concepts.
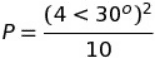
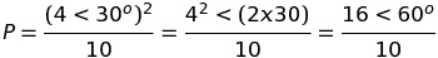
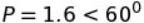 Do i need to divde the 60^o by 10 aswell
Do i need to divde the 60^o by 10 aswell