- #1
- 2,486
- 9,720
- TL;DR Summary
- NASA's Insight lander has been on Mars for 2 years.
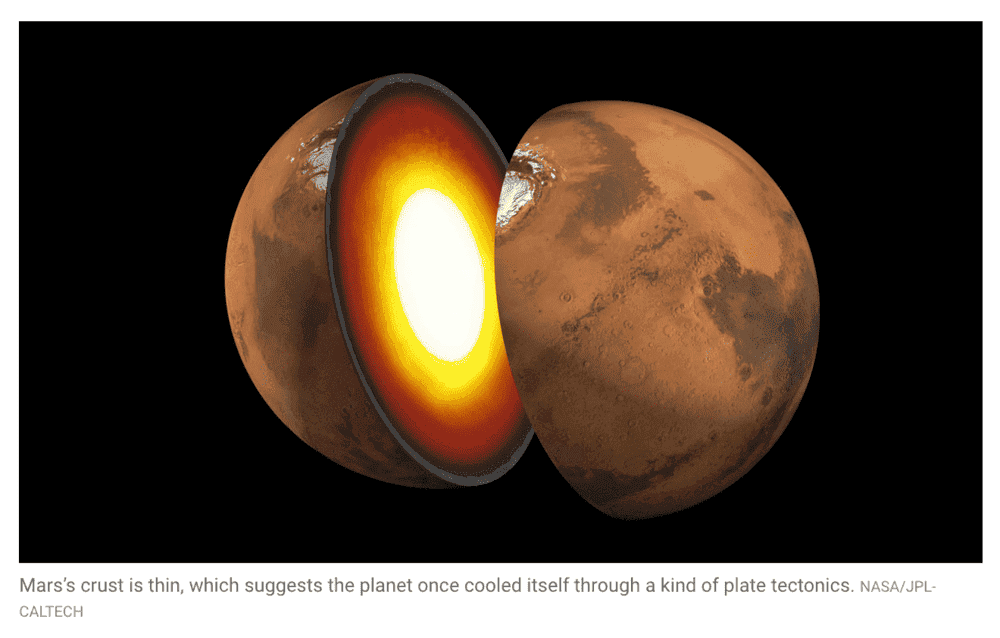
Its geological sensors indicate Mars has a thinner than expected crust, a cooler then expected mantle, and a large liquid core.
I have long been intrigued about what's going on inside Mars.
It shows signs of having had a very dynamic past, huge impact craters, huge volcanoes, massive systems of fissures and valleys.
Some think that it went through a period of plate tectonics and had a geological dynamo that generated a global magnetic field protecting its atmosphere from erosion due to the solar wind.
Science magazine news article here.
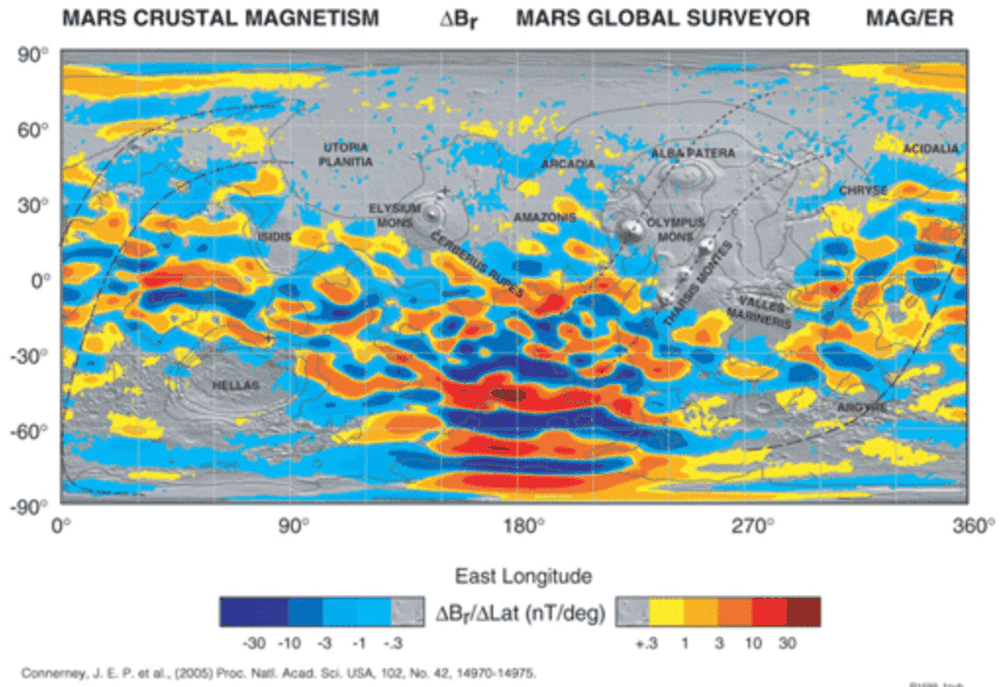
On Earth, a geological dynamo and plate tectonics (along with an alternation of the magnetic field) results in a pattern of stripes in the crust as new crust is exuded where the new crust is generated as the crust spreads apart.
This was found on Mars several years ago:
It shows signs of having had a very dynamic past, huge impact craters, huge volcanoes, massive systems of fissures and valleys.
Some think that it went through a period of plate tectonics and had a geological dynamo that generated a global magnetic field protecting its atmosphere from erosion due to the solar wind.
Science magazine news article here.
The results, some debuting this month at an online meeting of the American Geophysical Union (AGU), show the planet’s crust is surprisingly thin, its mantle cooler than expected, and its large iron core still molten. The findings suggest that in its infancy, Mars efficiently shed heat—perhaps through a pattern of upwelling mantle rock and subducting crust similar to plate tectonics on Earth. “This may be evidence for a far more dynamic crust formation in Mars’s early days,” says Stephen Mojzsis, a planetary scientist at the University of Colorado, Boulder, who is unaffiliated with the mission.
On Earth, a geological dynamo and plate tectonics (along with an alternation of the magnetic field) results in a pattern of stripes in the crust as new crust is exuded where the new crust is generated as the crust spreads apart.
This was found on Mars several years ago: