Discussion Overview
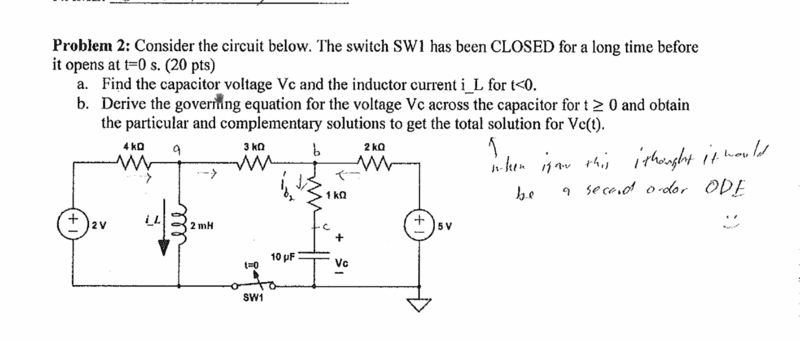
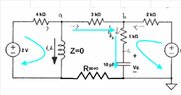
The discussion revolves around deriving the governing equation for the voltage \( V_c \) across a capacitor in a circuit involving resistors and an inductor. Participants explore the implications of opening a switch in the circuit and the resulting current behavior, with references to Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL).
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- Some participants express confusion about the current \( I_c \) through the circuit when the switch opens, noting that it may not be the same throughout the circuit.
- There are questions regarding the interpretation of terms in the KVL equation, particularly the second term, with suggestions that it may refer to a specific resistor value.
- Some participants assert that the problem is oddly stated, particularly regarding the time of interest for steady state conditions.
- There is a discussion about whether the resistors in the circuit have the same current, with differing opinions on this matter.
- Participants debate the possibility of current flowing through a resistor when the switch is opened, with some arguing that the circuits become isolated.
- There are claims that without a return path, there can be no current in certain parts of the circuit, leading to discussions about the implications for voltage and current at specific nodes.
- One participant proposes a formula for \( V_c \) based on the behavior of the circuit over time.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express multiple competing views regarding the behavior of current and voltage in the circuit, particularly when the switch is opened. There is no consensus on the implications of the circuit configuration or the correctness of the KVL and KCL applications.
Contextual Notes
Participants note limitations in the problem statement and the need for clarity on the definitions and assumptions regarding the circuit components and their interactions.