- #1
TheDudeTR
- 5
- 0
- Homework Statement
- i did not understand free body diagram in this question
- Relevant Equations
- F = ma
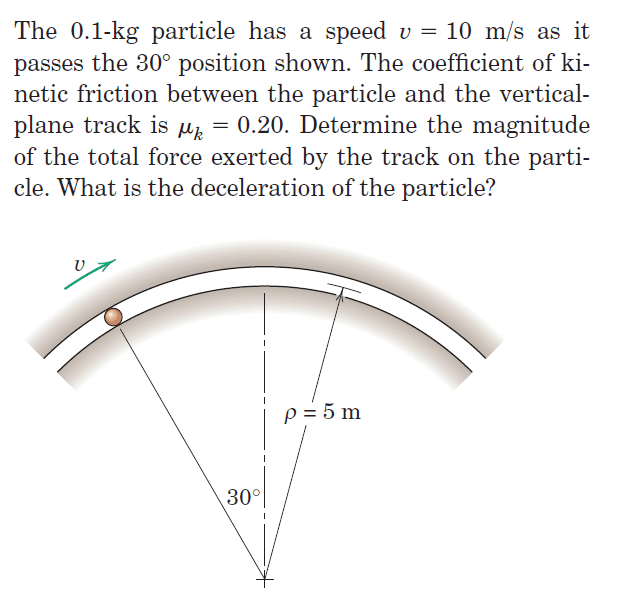
This is the question.
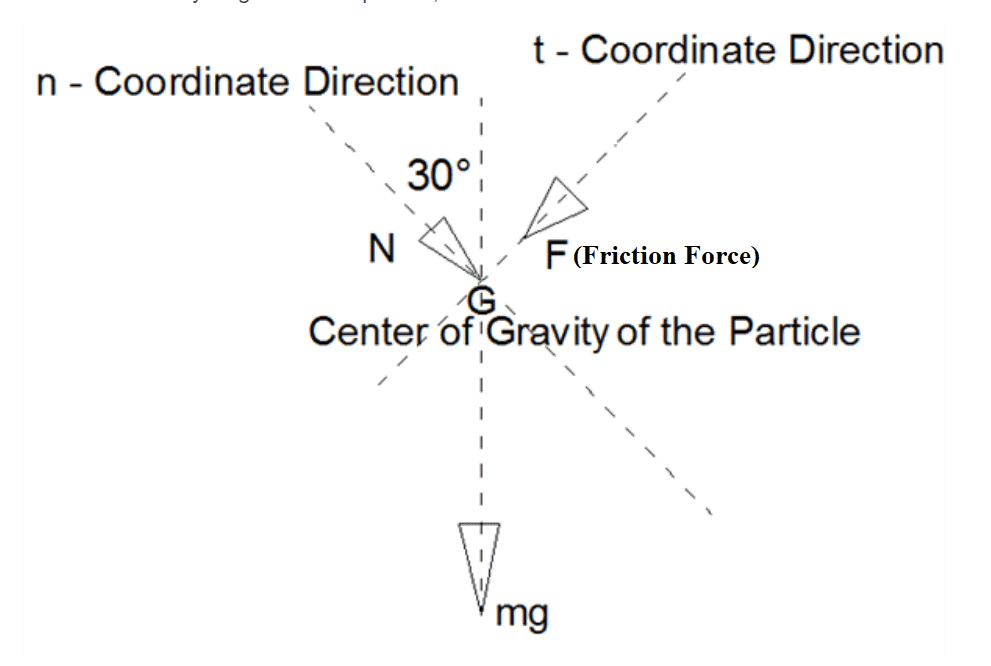
This is the FBD in the solution given. What i didn't understand is the sense of normal force. in the question mg force pulls particle down and according to my logic normal vector should be upwards in this conditions. but it is downwards in the given FBD. when i try to solve question with my own way result is different because of in the question it takes normal axis equations as (N+mg.cos30=m*a) and i took it as (-N+mg.cos30=m*a ) where am i wrong? can you help me please.
This is the FBD in the solution given. What i didn't understand is the sense of normal force. in the question mg force pulls particle down and according to my logic normal vector should be upwards in this conditions. but it is downwards in the given FBD. when i try to solve question with my own way result is different because of in the question it takes normal axis equations as (N+mg.cos30=m*a) and i took it as (-N+mg.cos30=m*a ) where am i wrong? can you help me please.