- #1
fight_club_alum
- 63
- 1
- TL;DR Summary
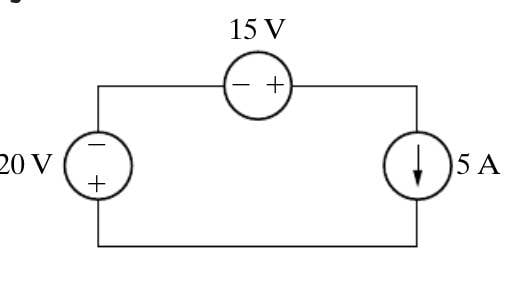
- How can I determine the voltage polarity of the current source in the circuit attached?
I am so sorry if I am posting this in the wrong forum; it is just not a homework problem, and I can't find the right place - it's more of a study help question.