- #1
akhurash
- 25
- 0
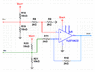
Hello, I need some help with a difference amplifier design I'm working on. The amplifier has to be work from a positive voltage supply only. I'm having a hard time getting it work with single supply voltage (it works when I use both negative and positive supply voltages). Both the inputs have a peak-to-peak voltage of about 2.2V (with the 2.5V DC bias). Also, the input voltages is not hitting the rail voltage (5V).
When I use a single supply the curve below 2.5V is railed and the positive voltage is not railed BUT the amplitude decreases dramatically. I think the single supply isn’t working because when the subtraction takes take it negates the DC bias voltage. Am I correct in this assumption? If so, how can I design a difference amplifier with just a single supply?
Attached is the difference amplifier circuit design.
When I use a single supply the curve below 2.5V is railed and the positive voltage is not railed BUT the amplitude decreases dramatically. I think the single supply isn’t working because when the subtraction takes take it negates the DC bias voltage. Am I correct in this assumption? If so, how can I design a difference amplifier with just a single supply?
Attached is the difference amplifier circuit design.