Discussion Overview
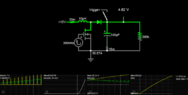
The discussion revolves around issues encountered in the design of a boost converter circuit intended to convert input voltages of 12V, 15V, and 24V to an output of 200V. Participants explore the behavior of the circuit, particularly the unexpected output voltage changes at various duty cycles and the implications of different design choices.
Discussion Character
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
- Experimental/applied
Main Points Raised
- The original poster (OP) reports irregular output voltages at specific duty cycles, questioning whether this behavior is typical for boost converters.
- Some participants inquire about the topology of the boost converter and whether it operates at a fixed frequency, suggesting that the switching frequency may influence performance.
- One participant emphasizes the importance of feedback control in preventing over-voltage and inductor saturation, suggesting that a controller is necessary for stable operation.
- Another participant notes that the output load appears to be essentially nonexistent, leading to high output voltages, and mentions the need to understand Continuous Conduction Mode (CCM) and Discontinuous Conduction Mode (DCM).
- There are discussions about the impact of the inductor's behavior and the role of diodes in the circuit, with some participants proposing modifications to improve performance.
- One participant shares a calculation indicating that a duty cycle of about 9% would be necessary to achieve the desired output voltage from a 12V input.
- Links to application reports from Texas Instruments are provided for further reading on feedback loop analysis for voltage-mode boost converters.
- The OP mentions testing a real-time system and expresses confusion about certain technical points raised by others.
- There are references to simulation results and the potential effects of reverse recovery in diodes on circuit performance.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the operation of the boost converter, particularly regarding the expected behavior at various duty cycles and the necessity of feedback control. The discussion remains unresolved, with multiple competing perspectives on the underlying issues and solutions.
Contextual Notes
Participants note the importance of understanding the operational modes of boost converters and the implications of load conditions on output voltage. There are references to potential risks of over-voltage and inductor saturation, but specific assumptions and dependencies on circuit parameters remain unclear.
Who May Find This Useful
Individuals interested in power electronics, particularly those designing or troubleshooting boost converters, may find this discussion relevant. It may also benefit those studying the theoretical aspects of converter operation and feedback control mechanisms.