Discussion Overview
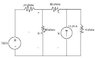
The discussion revolves around solving for voltages V_1 and V_2 in a circuit using the mesh current method, specifically through the application of supermesh analysis. Participants are exploring the calculations and relationships between current and voltage in the context of circuit analysis.
Discussion Character
- Homework-related
- Mathematical reasoning
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- The initial equations for mesh currents I1 and I2 are presented, with calculations leading to I1 = 3.10 A and I2 = 2 A.
- V_1 is calculated using the formula V = IR, resulting in V_1 = 88 V based on the current difference of 1.1 A across an 80-ohm resistor.
- The participant expresses uncertainty about calculating V_2, initially proposing to use the power equations and KVL.
- Another participant points out that V_2 is the voltage across the current source and suggests considering other elements in parallel with the current source.
- There is a clarification regarding the resistor in parallel with the current source, with a focus on the 4-ohm resistor and its relationship to the current source's voltage.
- It is noted that the voltage across the parallel resistor is the same as that across the current source, leading to a potential calculation for V_2 based on the current through that resistor.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the calculation of V_2, with some uncertainty about the elements involved and the correct approach to take. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the exact value of V_2 and the methods used to derive it.
Contextual Notes
There are limitations in the clarity of the circuit elements and their configurations, which may affect the calculations. The assumptions regarding the relationships between voltage and current in parallel components are also not fully resolved.
Who May Find This Useful
This discussion may be useful for students and practitioners interested in circuit analysis, particularly those learning about mesh current methods and the implications of circuit components in parallel.