SUMMARY
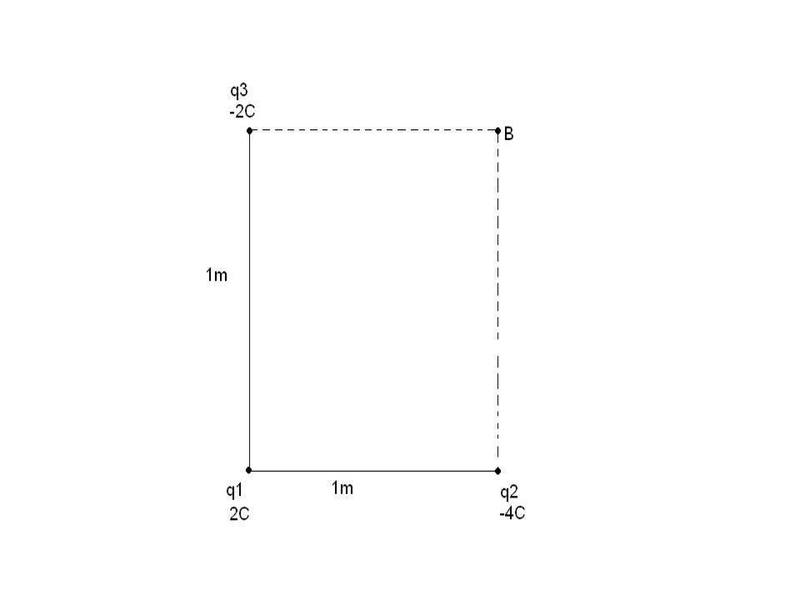
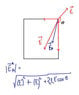
The discussion focuses on calculating the electric field intensity at point B due to three point charges: q1 = 2C, q2 = -4C, and q3 = -2C. The formula used for electric field intensity is E = (1/4πε0)(q/r³)r, with ε0 = 8.854 × 10-12 Farads/m. Participants clarify that the charges should be in nanocoulombs (nC) rather than coulombs (C), and they discuss the correct method for finding the resultant electric field intensity, emphasizing vector subtraction and the significance of angles between vectors. The final resultant electric field intensity is calculated to be approximately 31.248 N/C.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of electric field intensity and Coulomb's law
- Familiarity with vector addition and subtraction
- Knowledge of units of charge (Coulombs vs. nanocoulombs)
- Basic grasp of trigonometry for resolving vector components
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation and application of Coulomb's law in electrostatics
- Learn about vector addition and subtraction in physics
- Explore the implications of charge units in electric field calculations
- Investigate the role of angles in vector resolution and resultant calculations
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in physics, particularly those focusing on electrostatics, as well as anyone involved in solving problems related to electric fields and forces.