SUMMARY
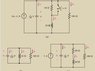
The voltage across the capacitor in the RLC circuit is determined to be 97.3 V through the application of nodal analysis. The equation used is 3 A - i(ind)/48 - i(res)/100 = v(cap), which highlights the relationship between current and voltage in the circuit. The discussion emphasizes the importance of maintaining consistent units across all terms in the equation to avoid confusion and errors in calculations. A suggestion is made to multiply the current source by the total effective resistance to find the voltage across the capacitor.
PREREQUISITES
- Nodal Analysis in electrical circuits
- Understanding of RLC circuit components
- Basic principles of voltage and current relationships
- Unit consistency in electrical equations
NEXT STEPS
- Study advanced Nodal Analysis techniques for complex circuits
- Learn about effective resistance in RLC circuits
- Explore methods for ensuring unit consistency in electrical calculations
- Investigate the impact of varying current sources on circuit behavior
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and anyone involved in analyzing RLC circuits and their voltage characteristics.