Homework Help Overview
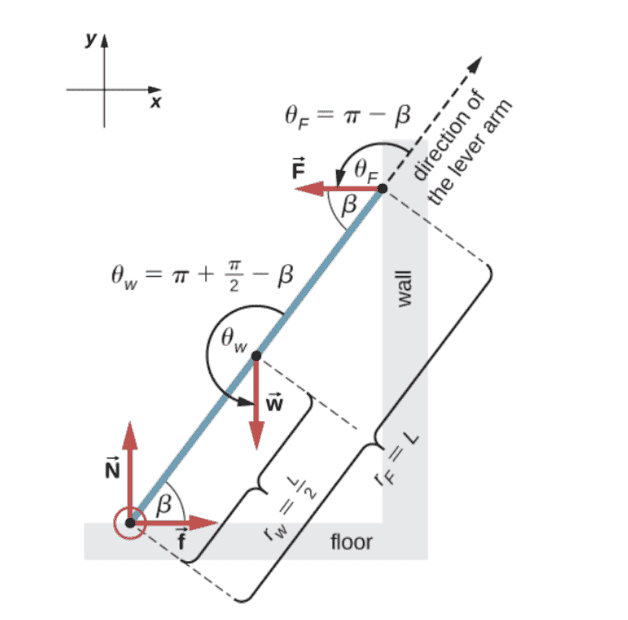
The discussion revolves around a ladder leaning against a frictionless wall and the floor, focusing on the forces acting on the ladder, particularly the force exerted by the wall and its relationship with static friction at the base. Participants are exploring the dynamics of the ladder's movement and the implications of static friction in this context.
Discussion Character
- Conceptual clarification, Assumption checking, Exploratory
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants are questioning how the force from the wall affects the ladder's movement and the role of static friction in preventing sliding. Some suggest that the force applied at the top of the ladder influences the entire structure, while others discuss the implications of the center of mass and the conditions for equilibrium.
Discussion Status
The discussion is active with various interpretations being explored. Some participants are providing insights into the mechanics of the situation, while others are raising questions about the assumptions made regarding the forces involved. There is no explicit consensus, but several productive lines of reasoning are being examined.
Contextual Notes
Participants note the constraints of the problem, such as the frictionless nature of the wall and the equilibrium conditions that must be satisfied. The discussion also highlights the limitations of static friction and the conditions under which the ladder might move.