- #1
jcw
- 6
- 0
Looking for some help with a rear brake caliper design.
The rear caliper bolts to a carrier that slides onto and rotates around an axle. An torque arm (motorcycle term) or brake stay is required to prevent the caliper from rotating when the rear brake is applied.
I have to figure a way to fabricate a brake stay and was trying to determine the forces involved and whether mounting the brake stay as far from the axle as possible is better than closer to the axle. I mean does the force on the bolts holding the brake stay in place increase as the distance from the axle decreases.
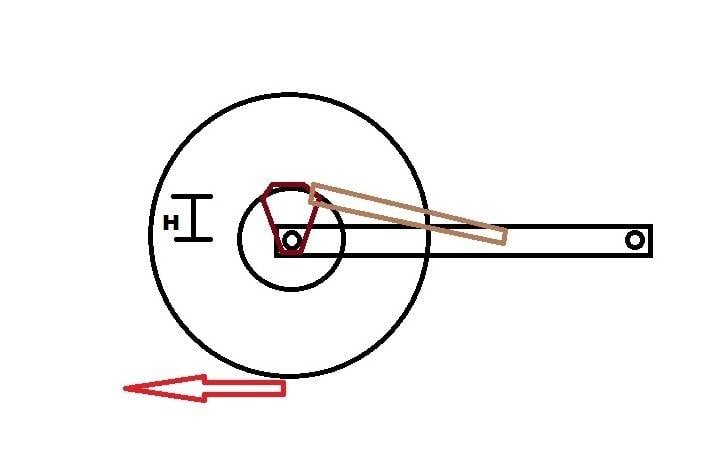
Thanks in advance!
The rear caliper bolts to a carrier that slides onto and rotates around an axle. An torque arm (motorcycle term) or brake stay is required to prevent the caliper from rotating when the rear brake is applied.
I have to figure a way to fabricate a brake stay and was trying to determine the forces involved and whether mounting the brake stay as far from the axle as possible is better than closer to the axle. I mean does the force on the bolts holding the brake stay in place increase as the distance from the axle decreases.
Thanks in advance!