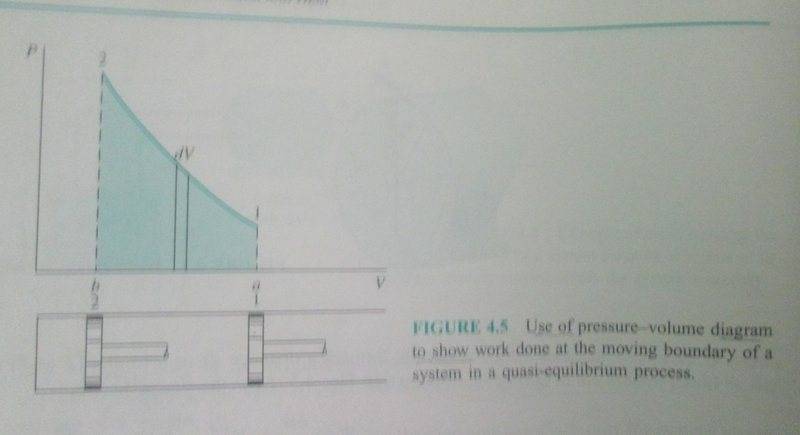
SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the graphical representation of gas compression in a closed system, specifically addressing whether the pressure-volume (P-V) diagram should always be non-linear. It is established that under isothermal conditions (constant temperature), the graph is non-linear. However, confusion arises regarding the shape of the curve when temperature decreases, with references made to the Ideal Gas Law (P * V = N * R * T) and polytropic processes (PV^n = C) as key equations for understanding the relationship between pressure, volume, and temperature during compression.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of the Ideal Gas Law (P * V = N * R * T)
- Knowledge of polytropic processes (PV^n = C)
- Familiarity with isothermal and non-isothermal gas compression
- Basic principles of thermodynamics and gas behavior
NEXT STEPS
- Study the implications of the Ideal Gas Law on gas behavior during compression
- Explore polytropic processes and their applications in thermodynamics
- Learn about isothermal versus adiabatic processes in gas compression
- Investigate graphical representations of P-V diagrams for various gas processes
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in thermodynamics, mechanical engineers, and anyone involved in the study of gas behavior in closed systems will benefit from this discussion.