- #1
matematikuvol
- 192
- 0
[tex]\oint_S \vec{A}\cdot d\vec{S}=\int_V div\vec{A}dv[/tex]
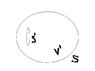
Suppose region where [tex]\vec{A}(\vec{r})[/tex] is diferentiable everywhere except in region which is given in the picture. Around this region is surface [tex]S'[/tex]. In this case Gauss theorem leads us to
[tex]\int_S \vec{A}\cdot d\vec{S}+\int_S \vec{A}\cdot d\vec{S}=\int_{V'} divAdv[/tex]
Am I right?
Suppose region where [tex]\vec{A}(\vec{r})[/tex] is diferentiable everywhere except in region which is given in the picture. Around this region is surface [tex]S'[/tex]. In this case Gauss theorem leads us to
[tex]\int_S \vec{A}\cdot d\vec{S}+\int_S \vec{A}\cdot d\vec{S}=\int_{V'} divAdv[/tex]
Am I right?
Last edited: