- #1
JC2000
- 186
- 16
Summary:: My understanding of integrators and the waveforms they generate is hazy.
The question I am trying to solve is : Sketch the output waveform for an inverting integrator if the input signal is a square wave with amplitude 5 V and frequency 1kHz where the product of Resistance and Capacitance is 1.
I have the following questions with regard to the question, integrators and the waveforms they generate.
1. I have derived the equation relating input and output voltages however I am unable to understand exactly how the current is flowing, how the capacitor is behaving etc within the circuit...
2. I believe that the result is a triangular waveform output. However I don't really understand why :
a. What function do you integrate for a square waveform?
b. What is happening physically within the circuit to cause such an output?
3. Under what conditions does a square waveform input result for the same circuit result in the following output waveforms (if at all) :
a. An increasing staircase waveform (upto saturation)
b. An inverted triangular waveform
c. decreasing staircase waveform
(Regarding Q3. I believe that these outputs have something to do with the time period you consider during integration but I am unsure about why or how this would happen)
Thank you for your time!
The question I am trying to solve is : Sketch the output waveform for an inverting integrator if the input signal is a square wave with amplitude 5 V and frequency 1kHz where the product of Resistance and Capacitance is 1.
I have the following questions with regard to the question, integrators and the waveforms they generate.
1. I have derived the equation relating input and output voltages however I am unable to understand exactly how the current is flowing, how the capacitor is behaving etc within the circuit...
2. I believe that the result is a triangular waveform output. However I don't really understand why :
a. What function do you integrate for a square waveform?
b. What is happening physically within the circuit to cause such an output?
3. Under what conditions does a square waveform input result for the same circuit result in the following output waveforms (if at all) :
a. An increasing staircase waveform (upto saturation)
b. An inverted triangular waveform
c. decreasing staircase waveform
(Regarding Q3. I believe that these outputs have something to do with the time period you consider during integration but I am unsure about why or how this would happen)
Thank you for your time!
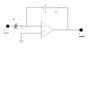
 I love it) said in the earlier post #4 about the current going into the op-amp and the voltages at the two terminals.
I love it) said in the earlier post #4 about the current going into the op-amp and the voltages at the two terminals.