- #1
eehelp150
- 237
- 0
Homework Statement
To analyze these circuits, we need to draw the current path right? I know that current can only flow one direction through a diode.
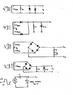
http://i.imgur.com/kipBcax.png
Homework Equations
N/A
The Attempt at a Solution
Are these paths correct? Green = positive, red = negative
1. Positive edge can only go through diode 1, so the positive edge gets clipped to +0.7V. Negative edge can only go through diode 2, so negative edge gets clipped to -0.7V
http://i.imgur.com/Sx8MvpY.png
2. Positive edge of top waveform can go through top diode. Negative edge of top waveform cannot.
Positive edge of bottom waveform cannot go through bottom diode. Negative can.
Results in rectified wave form capped at 5.6V due to the Zener
http://i.imgur.com/XYa5e5H.png
3. Don't really know how this one works
4. The waveform for this would 'start' from 4.3V (5V - 0.7V) and get clipped at 12.74V (14.14V - 2x0.7V)
http://i.imgur.com/iTStF8O.png
5. The positive edge can go through the diode but the negative one cannot. What would the waveform look like?
http://i.imgur.com/DoMnqwM.png
Am I doing these questions right?