SUMMARY
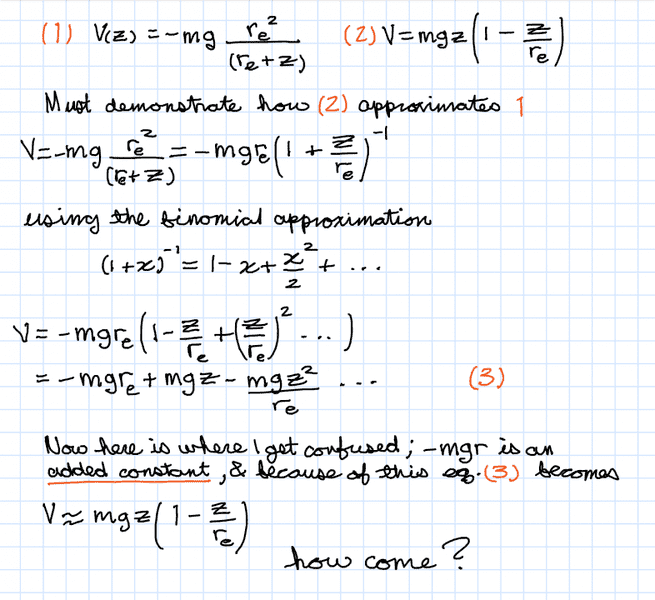
The discussion centers on the role of an additive constant in potential energy calculations, specifically in the context of gravitational potential energy. The two formulas discussed are U=mgz, which uses the Earth's surface as a reference point, and a formula with an additive constant that sets the potential energy to zero at z=0. The additive constant allows for flexibility in defining the reference point of potential energy, as it can be adjusted without affecting the physical differences in potential energy between two points. This concept is crucial for understanding how potential energy is calculated in various scenarios.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of gravitational potential energy
- Familiarity with the concept of reference points in physics
- Basic knowledge of calculus, specifically indefinite integrals
- Knowledge of the formula for gravitational force, U=mgz
NEXT STEPS
- Study the implications of reference points in potential energy calculations
- Learn about the concept of zero potential energy in different contexts
- Explore the mathematical properties of indefinite integrals and additive constants
- Investigate how potential energy is applied in various physics problems and real-world scenarios
USEFUL FOR
Students studying physics, particularly those focusing on mechanics and energy concepts, as well as educators looking to clarify the concept of additive constants in potential energy calculations.