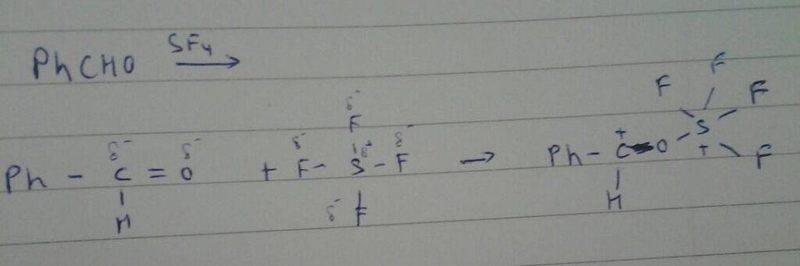SUMMARY
The reaction between benzaldehyde (PhCHO) and sulfur tetrafluoride (SF4) involves the participation of lone pairs on oxygen and pi electrons in the benzene ring. The mechanism indicates that the positive carbon is stabilized by the benzene ring and oxygen, while the sulfur atom acquires a negative charge due to electron accumulation. Understanding the stability of the sulfur and the charge distribution is crucial for elucidating the reaction mechanism. This analysis provides a clear pathway for constructing the reaction mechanism effectively.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of organic chemistry mechanisms
- Familiarity with benzaldehyde (PhCHO) and its properties
- Knowledge of sulfur tetrafluoride (SF4) reactivity
- Concept of resonance in aromatic compounds
NEXT STEPS
- Research the detailed mechanism of PhCHO and SF4 reactions
- Study the stability and reactivity of sulfur compounds
- Learn about charge distribution in organic reactions
- Explore resonance structures in aromatic systems
USEFUL FOR
Chemistry students, organic chemists, and researchers interested in reaction mechanisms involving aromatic compounds and sulfur chemistry.