SUMMARY
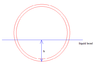
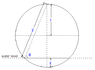
The discussion focuses on calculating the height submerged (h) of a hollow, non-open-ended cylinder floating in a liquid. Participants emphasize the relationship between the cylinder's weight (M), the density of the liquid (ρ), and the volume of the submerged part (V). The key formula derived is based on Archimedes' principle, where the cylinder floats when M = ρV. The submerged volume is expressed as a function of height, with the area of the cylinder's end (A) and its length (L) being critical components in the calculations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Archimedes' principle
- Basic calculus for volume integration
- Knowledge of geometric properties of cylinders
- Familiarity with fluid density concepts
NEXT STEPS
- Learn how to derive the submerged volume of a cylinder using calculus
- Study the relationship between weight and submerged volume in fluid mechanics
- Explore the concept of circular segments in geometry for submerged calculations
- Investigate the use of rectangular coordinates in volume integration
USEFUL FOR
Students and professionals in physics, engineering, and mathematics, particularly those focusing on fluid mechanics and buoyancy calculations.