Rambo7
- 1
- 0
- Homework Statement
- "The strip conductor LB that is common to both circuits has an inductance of 100mH. The resistance of the common trace portion is negligibly small. The amplitude of u2 is 10V and f=1MHz. Due to the galvanic coupling via the trace component LB, there is an interference voltage at the measuring amplifier. Determine the interference voltage."
- Relevant Equations
- voltage divider
Hello everyone,
I have this circuit and I need to determine the interference voltage.

I am not sure, where the interference voltage is applied and how to determine it. I think the interference voltage is uv nad my equivalent circuit looks like this:
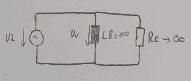
Am I in heading into the right direction? Do I need to consider R2 as well? I would be very thankful if you help me solving this.
I have this circuit and I need to determine the interference voltage.
I am not sure, where the interference voltage is applied and how to determine it. I think the interference voltage is uv nad my equivalent circuit looks like this:
Am I in heading into the right direction? Do I need to consider R2 as well? I would be very thankful if you help me solving this.