SUMMARY
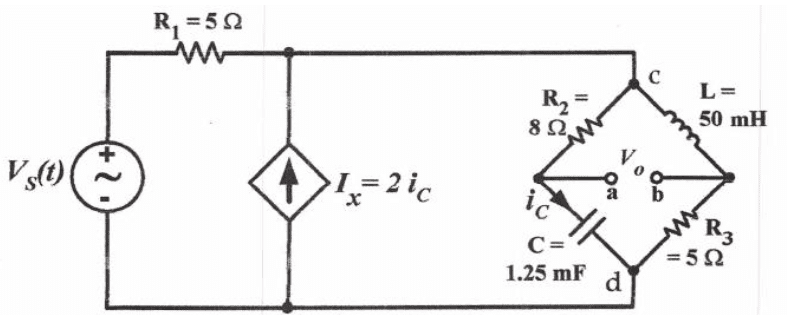
To determine voltage and current in an RLC circuit, start by calculating the reactance values, specifically the inductive reactance (XL) and capacitive reactance (XC), using the angular frequency (omega = 100). Employ Thevenin source transformations to simplify the circuit, converting the voltage source in series with a 5-ohm resistor into a current source with a parallel 5-ohm resistor. This approach allows for easier application of Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL) equations to find branch currents and voltages. Ultimately, use phasors to analyze the circuit and derive the necessary electrical parameters.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of RLC circuit theory
- Familiarity with Thevenin source transformations
- Knowledge of phasor analysis in AC circuits
- Proficiency in applying Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)
NEXT STEPS
- Study Thevenin's theorem and its applications in circuit analysis
- Learn about calculating inductive and capacitive reactance in AC circuits
- Explore phasor representation and analysis techniques
- Review examples of KVL and KCL applications in RLC circuits
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and professionals involved in AC circuit analysis and RLC circuit optimization.