Discussion Overview
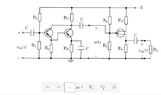
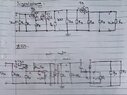
The discussion revolves around the input and output impedance of a circuit involving multiple transistors, specifically focusing on the small signal model and how different amplifier stages interact with each other. Participants explore the implications of loading effects between stages and the calculations involved in determining impedances.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant expresses confusion about rewriting a circuit with three transistors into a small signal model.
- Another participant questions whether the output impedance of the first amplifier stage is affected by the input impedance of the second stage.
- Some participants suggest that the input impedance of the second stage loads the output drive of the first stage, but this does not change the output impedance of the first stage.
- There is a discussion about the implications of the FET's infinite input impedance on the current flow from the first amplifier.
- A participant provides a detailed explanation of how to analyze the input and output impedances, mentioning specific resistor values and configurations.
- Another participant confirms the correctness of expressions related to voltage calculations between the two amplifiers.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on how the input and output impedances interact, with some suggesting that loading effects do not alter the output impedance while others explore the implications of these interactions. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the specific effects of one amplifier stage on another.
Contextual Notes
Participants reference specific circuit analysis techniques and models, indicating that assumptions about transistor input and output impedances may vary. There is mention of the complexity introduced by DC biasing and the use of interstage isolation capacitors.
Who May Find This Useful
This discussion may be useful for individuals studying circuit design, particularly those interested in small signal analysis and the interactions between multiple amplifier stages in transistor circuits.