shawisco
- 1
- 0
Hi all:
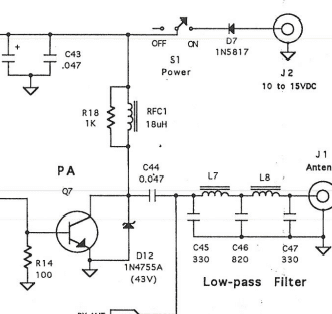
I am a new member here with my first post. I am an adult learner trying to self-teach RF electronics. I have been working through David Rutledge's Electronics of Radio, while building the NorCal 40A transceiver.
I am getting caught up on understanding the Class C RF power amplifier circuit.
I don't understand how the output voltage across the collector of Q7 can be more than twice the DC supply voltage (12VDC). I assume that the reactive components--such as RFC1--are storing energy?
Any help would be appreciated. I have included the schematic below.
I am a new member here with my first post. I am an adult learner trying to self-teach RF electronics. I have been working through David Rutledge's Electronics of Radio, while building the NorCal 40A transceiver.
I am getting caught up on understanding the Class C RF power amplifier circuit.
I don't understand how the output voltage across the collector of Q7 can be more than twice the DC supply voltage (12VDC). I assume that the reactive components--such as RFC1--are storing energy?
Any help would be appreciated. I have included the schematic below.