Homework Help Overview
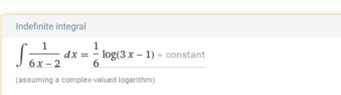
The discussion revolves around the integration of functions of the form \(\dfrac{1}{ax+b}\), specifically focusing on the integral \(\int \dfrac{1}{6x-2} dx\). Participants are examining conflicting interpretations from different computational tools, namely Wolfram and Symbolab, regarding the treatment of logarithmic functions in this context.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Assumption checking, Conceptual clarification
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants are comparing the approaches of Wolfram and Symbolab, questioning the validity of each based on definitions of logarithmic functions and their domains. There is discussion about the implications of using absolute values in logarithmic expressions and the relevance of complex versus real logarithms.
Discussion Status
The discussion is ongoing, with participants exploring different interpretations of the integration results. Some have noted that both approaches can be mathematically correct under different conditions, particularly regarding the domains of the logarithmic functions involved.
Contextual Notes
There is mention of the conditions under which the two answers align, specifically noting that the results differ for values of \(x\) less than \(1/3\). Participants are also considering the implications of using absolute values in their expressions.