Discussion Overview
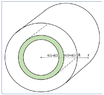
The discussion centers on the interpretation of thermal power in a system consisting of two concentric cylinders separated by an insulating material, where one cylinder contains a thermal source and the other acts as a thermal sink. Participants explore the implications of positive and negative power readings in relation to energy transfer between the internal cylinder and the external environment.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant describes a system with a thermal source in the internal cylinder and a thermal sink outside, noting that the internal cylinder has positive power while the external system has negative power.
- Another participant questions the meaning of "thirsty" in the context of the thermal sink and seeks clarification on the interpretation of the power signs.
- Clarifications are made regarding the configuration of the cylinders and the direction of heat transfer, with some participants suggesting that the positive power indicates heat transfer from the internal cylinder to the outer cylinder rather than directly to the environment.
- Concerns are raised about whether the system is in a steady state and the implications of the net energy transfer being zero, while heat flow remains positive.
- One participant proposes that the system is gaining energy, suggesting that it attracts heat from its surroundings to compensate for a lack of energy, while another questions if this aligns with the concept of the heat sink.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing interpretations of the thermal dynamics at play, particularly regarding the direction of heat flow and the implications of the power readings. No consensus is reached on the overall energy behavior of the system.
Contextual Notes
There are unresolved questions about the steady state of the system, the definitions of terms used (such as "heat sink"), and the assumptions made regarding energy transfer and temperature conditions.