SUMMARY
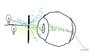
The discussion centers on how the human eye differentiates light from multiple point sources, specifically addressing the behavior of photons emitted from a pinhole light source. It is established that the lens of the eye converges light rays from each point source to a specific point on the retina, allowing for the perception of directionality. The angle at which light rays enter the eye is crucial for identifying the source of light, as they strike different areas of the retina based on their origin. This mechanism enables the eye to distinguish between closely positioned light sources despite overlapping photon paths.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic optics principles
- Knowledge of human eye anatomy, particularly the lens and retina
- Familiarity with photon behavior and light dispersion
- Concept of visual perception and how stimuli are processed
NEXT STEPS
- Research the anatomy and function of the human eye, focusing on the lens and retina
- Study the principles of optics, including light rays and convergence
- Explore the concept of visual perception and how the brain interprets light stimuli
- Investigate the physics of photons and their behavior in different mediums
USEFUL FOR
Students of optics, vision scientists, educators in biology and physics, and anyone interested in the mechanics of human vision and light perception.