metallica007
- 8
- 0
Hi everyone
When using the concept of the conservation of the linear momentum ΣPi = ΣPf to solve a problem, should I consider the the direction of the velocity? For Example, the following problem
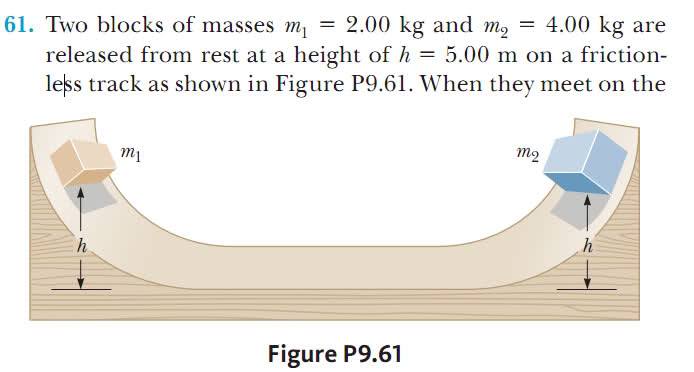
which one of the following equations is correct?
m1v0+m2v0=m1v1+m2v2
or
m1v0-m2v0=-m1v1+m2v2
note: both of the blocks have the same intial velocity (v0) because the surface is frictionless.
When using the concept of the conservation of the linear momentum ΣPi = ΣPf to solve a problem, should I consider the the direction of the velocity? For Example, the following problem
which one of the following equations is correct?
m1v0+m2v0=m1v1+m2v2
or
m1v0-m2v0=-m1v1+m2v2
note: both of the blocks have the same intial velocity (v0) because the surface is frictionless.