10-D King
- 5
- 0
1. The equilibrium bond length r0 in ion components (or salts) can always be obtained from the tabulated values of cationic, r+, and anionic radii, r-, respectively as
r0=r+ + r-
Show how on this basis, and that above (refering to the first part of the problem where i was to verify that the magdelung constants divided by the number of ions in one formula unit is constant(A/v)), the Born-Lande and Borne-Mayer equations become the Kapustinskii equations.
2. Borne-Lande equation
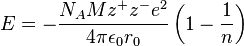
Borne-Mayer Equation
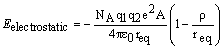
3. When carrying out the first part of the equation i obtained an average (A/v) value of 0.839 and i can easily derive the actual Borne equations but no matter what i try i can't get a decent answer for the derivation of the Kapustinskii equation
Any assistance would be of great appreciation.
r0=r+ + r-
Show how on this basis, and that above (refering to the first part of the problem where i was to verify that the magdelung constants divided by the number of ions in one formula unit is constant(A/v)), the Born-Lande and Borne-Mayer equations become the Kapustinskii equations.
2. Borne-Lande equation
Borne-Mayer Equation
3. When carrying out the first part of the equation i obtained an average (A/v) value of 0.839 and i can easily derive the actual Borne equations but no matter what i try i can't get a decent answer for the derivation of the Kapustinskii equation
Any assistance would be of great appreciation.