Click For Summary
SUMMARY
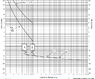
The maximum interrupting time for FW/HFW Molded-Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) is determined by analyzing the time-current curves specific to the breaker model. For a 40 Amp MCCB, the maximum instantaneous fault clearing times are calculated as 5.5 seconds at 10X (400 Amps) and 4.6 seconds at 9X (360 Amps). It is crucial to ensure that the breaker settings coordinate with downstream elements, such as motors and cables, to prevent overheating and ensure protection during overload conditions. The coordination of time-current curves is essential for effective circuit protection.
PREREQUISITES- Understanding of Molded-Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs)
- Familiarity with time-current curves and their interpretation
- Knowledge of motor characteristics, including Locked Rotor Current (LRA)
- Basic electrical engineering principles related to overload protection
- Study the time-current curves for specific MCCB models to understand their performance
- Learn about motor protection settings and their implications on circuit design
- Research the coordination of electrical protection devices in motor applications
- Explore the differences between Long Time, Short Time, and Instantaneous trip settings in MCCBs
Electrical engineers, circuit designers, and maintenance professionals involved in motor protection and MCCB applications will benefit from this discussion.