SUMMARY
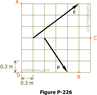
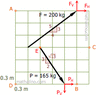
The discussion focuses on calculating the moment of forces F = 200 kg and P = 165 kg about points A, B, C, and D, using the principles of static equilibrium. The numbers 5, 4, and 3 refer to the dimensions of a right triangle formed by the vector representation of force F, where the horizontal leg measures 4 units, the vertical leg measures 3 units, and the hypotenuse, representing the resultant force, measures 5 units. This triangle is crucial for determining the moment arm and calculating the moments about the specified points.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of static equilibrium principles
- Knowledge of moment calculations in physics
- Familiarity with vector representation of forces
- Basic geometry, specifically right triangles
NEXT STEPS
- Study the calculation of moments in static systems
- Learn about vector decomposition in physics
- Explore the application of trigonometry in force analysis
- Review examples of moment calculations about various points
USEFUL FOR
Students in physics, engineers working with static structures, and anyone involved in mechanics or force analysis will benefit from this discussion.