SUMMARY
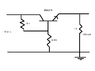
The output impedance of a pass transistor, specifically an emitter-follower configuration, can be calculated using the relationship between the output voltage and the short circuit current. Given a beta (β) value of 200, the output impedance is approximately equal to the output impedance of the bias circuit supplying the base current divided by β. In this case, the output impedance of the bias network, calculated from the parallel combination of a 10k and 6.8k resistor, is about 4047.6 ohms, leading to an approximate output impedance of 20.24 ohms. When a load resistor is added, the output impedance can be measured by analyzing the voltage drop across the load resistor.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) operation
- Familiarity with emitter-follower circuit configurations
- Knowledge of Thevenin equivalent circuits
- Ability to perform calculations involving parallel resistances
NEXT STEPS
- Study the characteristics of Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs) and their equivalent circuit models
- Learn about Thevenin's theorem and its application in circuit analysis
- Explore the concept of output impedance in various transistor configurations
- Investigate the effects of load resistors on circuit performance and impedance measurements
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and anyone involved in analyzing or designing transistor-based circuits, particularly those working with pass transistors and emitter followers.