quantumsimulation
- 1
- 1
As I listen to lectures trying to explain the universe based on the laws of physics, it makes no sense and it can be all over the place with holes and gaps. Dark this or a catastrophe here.So the physical laws seem to be lacking when it comes to explaining the nature of reality. We can use these laws as an approximation of reality as Cognitive Scientist Donald Hoffman says but they just help us navigate a much bigger and more expansive reality we can't fully explain. A few years ago, this would be conjecture but today I would say it's more likely that we live in a simulation of quantum information instead of a universe built on physical laws. If you apply Occam's Razor it just makes sense and it's easier to explain like in Professor Seth Lloyd's book "Programming the Universe" where hesays the universe isn't like a quantum computer but it is a quantum computer. Here's some evidence that supports this:
1. The Holographic universe and the Bekenstein Bound.
How can you have a volume of space filled with matter when the volume of space is proportional to a 2D surface area on it's boundary?
You have Physicist now who think spacetime is an quantum error correcting code. Here's a great talk by John Preskill.
This would also explain why spacetime is so vast. You need a lot of physical qubits(space) to encode the universe on logical qubits.
There was another recent paper that was fascinating.
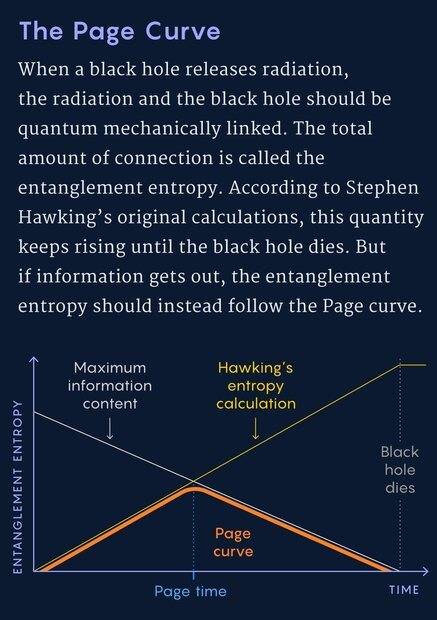
Basically, you have something called the Page Curve which shows that information can escape a black hole.
https://www.quantamagazine.org/the-most-famous-paradox-in-physics-nears-its-end-20201029/
So, if a plane fell into a black hole, the information about the plane would be on the 2D event horizon. When Hawking Radiation escaped, it would contain information about the plane but it would be encrypted. Replica wormholes would connect the Hawking Radiatian and the interior of the black hole via entanglement. If spacetime forms on these replica wormholes and spacetime is an quantum error correcting code like John Preskill says, then the error correcting code could decrypt the information from the black hole.
You have a simple explanation of reality but you would have to accept that the universe is a simulation of information.
1. The Holographic universe and the Bekenstein Bound.
How can you have a volume of space filled with matter when the volume of space is proportional to a 2D surface area on it's boundary?
You have Physicist now who think spacetime is an quantum error correcting code. Here's a great talk by John Preskill.
This would also explain why spacetime is so vast. You need a lot of physical qubits(space) to encode the universe on logical qubits.
There was another recent paper that was fascinating.
Basically, you have something called the Page Curve which shows that information can escape a black hole.
He(Don Page) considered an aspect of the process that had been relatively neglected: quantum entanglement. The emitted radiation maintains a quantum mechanical link to its place of origin. If you measure either the radiation or the black hole on its own, it looks random, but if you consider them jointly, they exhibit a pattern. It’s like encrypting your data with a password. The data without the password is gibberish. The password, if you have chosen a good one, is meaningless too. But together they unlock the information. Maybe, thought Page, information can come out of the black hole in a similarly encrypted form.
Page calculated what that would mean for the total amount of entanglement between the black hole and the radiation, a quantity known as the entanglement entropy. At the start of the whole process, the entanglement entropy is zero, since the black hole has not yet emitted any radiation to be entangled with. At the end of the process, if information is preserved, the entanglement entropy should be zero again, since there is no longer a black hole. “I got curious how the radiation entropy would change in between,” Page said.
Initially, as radiation trickles out, the entanglement entropy grows. Page reasoned that this trend has to reverse. The entropy has to stop rising and start dropping if it is to hit zero by the endpoint. Over time, the entanglement entropy should follow a curve shaped like an inverted V. Page calculated that this reversal would have to occur roughly halfway through the process, at a moment now known as the Page time. This is much earlier than physicists assumed. The black hole is still enormous at that point — certainly nowhere near the subatomic size at which any putative exotic effects would show up. The known laws of physics should still apply. And there is nothing in those laws to bend the curve down.
Over the past two years, physicists have shown that the entanglement entropy of black holes really does follow the Page curve, indicating that information gets out. They did the analysis in stages. First, they showed how it would work using insights from string theory. Then, in papers published last fall, researchers cut the tether to string theory altogether.
https://www.quantamagazine.org/the-most-famous-paradox-in-physics-nears-its-end-20201029/
So, if a plane fell into a black hole, the information about the plane would be on the 2D event horizon. When Hawking Radiation escaped, it would contain information about the plane but it would be encrypted. Replica wormholes would connect the Hawking Radiatian and the interior of the black hole via entanglement. If spacetime forms on these replica wormholes and spacetime is an quantum error correcting code like John Preskill says, then the error correcting code could decrypt the information from the black hole.
You have a simple explanation of reality but you would have to accept that the universe is a simulation of information.