Emanuel Silva
- 5
- 0
Applying Bernoulli, Does the term ρ*g*h matters ? I am trying to select a fan
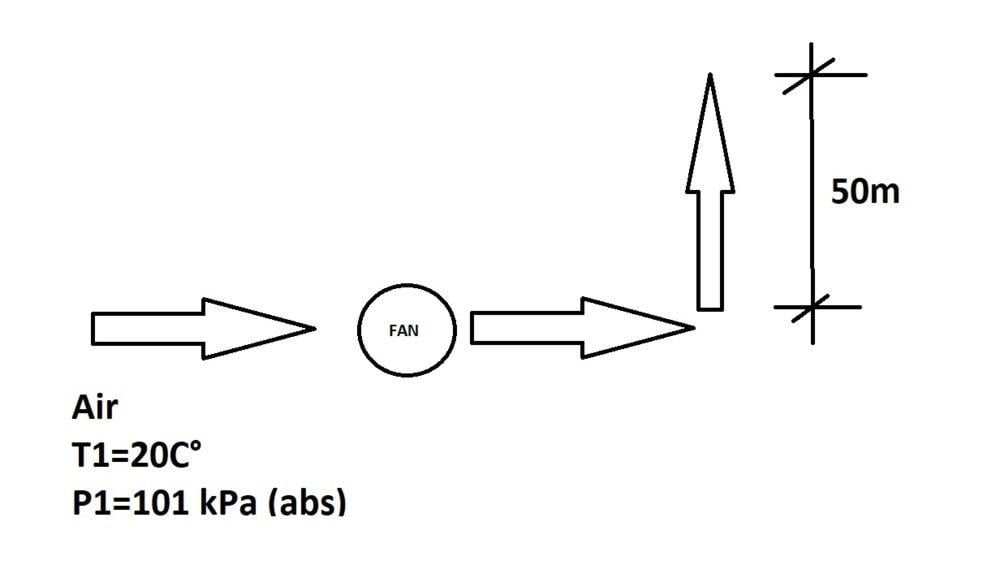
This discussion centers on the selection of a fan for extracting air from bathrooms and discharging it onto a roof, specifically addressing the impact of a 50-meter vertical air column. Participants conclude that while the fan must overcome gravity, the atmospheric pressure gradient effectively cancels the energy required to push the exhaust air upward. The consensus is that the height of the air column is of secondary importance, and factors such as viscosity and fan specifications should be prioritized in the selection process.
PREREQUISITESHVAC engineers, building contractors, and anyone involved in designing effective ventilation systems for residential or commercial spaces.
cjl said:I don't really understand what you're trying to do here - could you provide some more details? What do you need the fan to do, and what does the 50m mean in your diagram?
osilmag said:Are you trying to push the air 50 meters high or to the left?
You could also reference the Gas Laws.
Short answer is "no". Yes, you have to push the air upward against gravity. But there is also a pressure gradient in the ambient atmosphere, lower pressure up high, higher pressure down low. The pre-existing pressure gradient exactly cancels the energy it would take to force your exhaust air up through the pipe against gravity.Emanuel Silva said:High, the horizontal trajectory is minimum, It is negligible in this case.
I am trying to extract air from some bathrooms and discharge it on the roof,
I need to select a fan (working point implies a pressure resistance and a flow), I know the flow, but should I consider the column of air in this selection?
I have searched many books for a mathematical explanation for this, but I have not found it and I always get people who tell me that the air column should be considered. Where could I find a mathematical explanation for this? any particular book? tjbriggs444 said:Short answer is "no". Yes, you have to push the air upward against gravity. But there is also a pressure gradient in the ambient atmosphere, lower pressure up high, higher pressure down low. The pre-existing pressure gradient exactly cancels the energy it would take to force your exhaust air up through the pipe against gravity.
Assuming your exhaust air is the same density as the ambient atmosphere.
It goes back to Archimedes and buoyancy. Air is neutrally buoyant in air.Emanuel Silva said:Where could I find a mathematical explanation for this? any particular book? t
It's easy to find 'people' who have no idea about Physics yet who have all sorts of funny notions. If you read what's in this thread, you'll see plenty of reasons why the height of the column is of secondary importance. You can take that as good information because they're Physicists and Engineers etc.Emanuel Silva said:I always get people who tell me that the air column should be considered.
I don't "disbelieve you" but doesn't the Potential Energy of the falling air outside cancel that out? You are normally pretty good on fluids so I hesitated to ask.Chestermiller said:If you are going to use Bernoulli, even with a viscous term included, you need to include the gravitational (potential energy) term.
I don't understand your term "falling air outside." My understanding is that the air outside the pipe is static. So there is a gravitation induced gradient of pressure in the outside air. This will turn out to just cancel the gravitation potential energy term in the Bernoulli equation for the air inside the pipe. But, in applying the Bernoulli equation to the air inside the pipe, the gravitational potential energy term should be included, and then be canceled with the outside air term later. It is true that, if the gravitation contribution to the pressure is neglected in both the air inside the pipe and the air outside, the final answer will come out correct.sophiecentaur said:I don't "disbelieve you" but doesn't the Potential Energy of the falling air outside cancel that out? You are normally pretty good on fluids so I hesitated to ask.
Edit: "What goes up must come down", as they say.Chestermiller said:I don't understand your term "falling air outside."
No, they can neglect it in this case.Chestermiller said:If you are going to use Bernoulli, even with a viscous term included, you need to include the gravitational (potential energy) term. However, it may not be too important.
See my post #13cjl said:No, they can neglect it in this case.