binbagsss
- 1,291
- 12
The question is: a conducting spherical shell of radius a rotates about the z axis with angular velocity ω, in a uniform magnetic field B= B_{0}\hat{z} . Find an expression for the EMF developed between:
i) the north pole and the equator (2 marks);
ii) the north pole and the south pole (1 mark).
I'm struggling picturing why there is 0 flux between the north pole and south pole and a non-zero flux between the north pole and the equator.
So first of all, by rotates about the z-axis, I interpret this as any axis passing through the centre of the sphere.
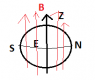
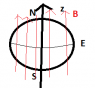
I have attached two diagrams, the first i take the north and south pole to be aligned with the z axis (vertical) and the second the north and south aligned horizontally.
- From the first diagram, I think, I undertand the flux comments above, but in the second diagram , I would get zero flux for both cases...
Questions:
- So by north and south pole do we mean north and south with respect to the z-axis, as the object is spherically symetric so otherwise how do you choose?
- I can also see that I have not used the fact that the object is a shell and not a dense sphere. Am I correct in thinking that the answers to i and ii remain unchanged if I were to replace the spherical shell with a sphere?
Many Thanks in advance for your assistance !
i) the north pole and the equator (2 marks);
ii) the north pole and the south pole (1 mark).
I'm struggling picturing why there is 0 flux between the north pole and south pole and a non-zero flux between the north pole and the equator.
So first of all, by rotates about the z-axis, I interpret this as any axis passing through the centre of the sphere.
I have attached two diagrams, the first i take the north and south pole to be aligned with the z axis (vertical) and the second the north and south aligned horizontally.
- From the first diagram, I think, I undertand the flux comments above, but in the second diagram , I would get zero flux for both cases...
Questions:
- So by north and south pole do we mean north and south with respect to the z-axis, as the object is spherically symetric so otherwise how do you choose?
- I can also see that I have not used the fact that the object is a shell and not a dense sphere. Am I correct in thinking that the answers to i and ii remain unchanged if I were to replace the spherical shell with a sphere?
Many Thanks in advance for your assistance !