- #1
Demon117
- 165
- 1
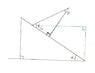
So I feel like a complete moron for asking this. I have never been very strong in geometry so I wondered if a few math folks could help me out. I am just looking for the angle relationships of gamma, alpha, and beta. This is just a small piece of a much larger analysis that I am doing.
I know that beta and gamma are related by [itex]\gamma=\beta - \frac{\pi}{2}[/itex], so if someone could push me in the right direction in determining the relationship between gamma and alpha. Thanks in advance.
I know that beta and gamma are related by [itex]\gamma=\beta - \frac{\pi}{2}[/itex], so if someone could push me in the right direction in determining the relationship between gamma and alpha. Thanks in advance.