- #1
josep233
- 1
- 0
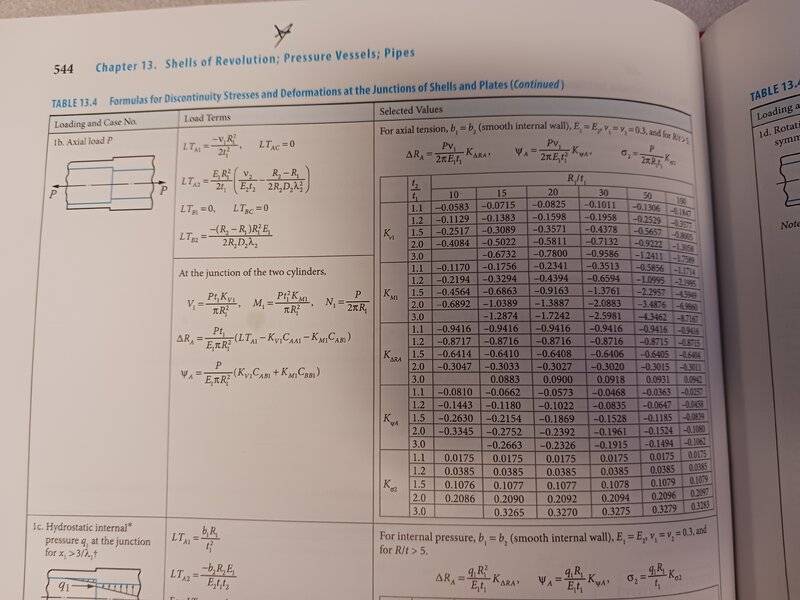
I am looking for clarification of some terms found in Roark's Formulas for Stress and Strain 9E. Table 13.4 pg 543 as well as preceding tables frequently reference R_A as the radius of common circumference. I take this to mean that this value could include any radius that both cylinders share through their thicknesses, but do not know for sure. To further confuse this, some tables say R_A = R_1. Does anyone with more exposure to this understand what R_A means?
Last edited by a moderator: