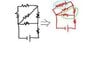
SUMMARY
This discussion focuses on simplifying complex circuit diagrams, specifically transforming a black diagram into series and parallel circuits. The user seeks guidance on combining resistors effectively, utilizing the equations for equivalent resistance in series (R_{eq} = R_1 + R_2 + ... + R_n) and parallel (\frac{1}{R_{eq}} = \frac{1}{R_1} + \frac{1}{R_2} + ...). Key insights include the importance of Kirchhoff's Law in analyzing current flow and achieving an accurate equivalent resistance. The final equivalent resistance for the circuit is determined to be approximately 3.575 ohms.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of series and parallel resistor configurations
- Familiarity with Kirchhoff's Law
- Knowledge of calculating equivalent resistance
- Basic circuit diagram interpretation skills
NEXT STEPS
- Study advanced circuit analysis techniques using Kirchhoff's Laws
- Learn about Thevenin's and Norton's theorems for circuit simplification
- Explore simulation tools like LTSpice for circuit modeling
- Investigate practical applications of equivalent resistance in real-world circuits
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, hobbyists working on circuit design, and professionals involved in circuit analysis and troubleshooting will benefit from this discussion.