Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around solving a circuit problem involving a complex source, specifically focusing on determining the circuit current, ##i_c(t)##, and the potential across the capacitor, ##v_c(t)##. Participants explore methods for analysis in both the time and frequency domains, including the use of phasors and complex impedance.
Discussion Character
- Homework-related
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Mathematical reasoning
Main Points Raised
- One participant expresses confusion about the problem and seeks clarification on the meanings of ##i_c(t)## and ##v_c(t)##, as well as the concept of adding a complex source.
- Another participant explains that ##i_c(t)## represents the circuit current and ##v_c(t)## represents the voltage across the capacitor, suggesting that working in the frequency domain with phasors is the easiest approach.
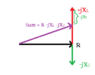
- A later reply provides specific calculations, stating the impedance of the capacitor as .025j and the voltage as 4.924-.868j, leading to a proposed expression for ##i_c(t)## as 5sin(20t+9.707deg.
- Some participants challenge the notion of negative impedance for capacitors, questioning whether it is appropriate to describe the impedance as negative, while others assert that capacitors inherently have a negative impedance.
- One participant mentions the phase difference between voltage and current through the capacitor, emphasizing the importance of understanding complex arithmetic and suggesting the use of sketches for clarity.
- Another participant proposes a different approach using complex voltage and impedance, leading to a calculation for reactive energy.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
There is no consensus on the characterization of capacitor impedance as negative, with some participants asserting it while others question the terminology. The discussion remains unresolved regarding the implications of negative impedance in this context.
Contextual Notes
Participants express varying levels of understanding and terminology regarding complex impedance and its implications in circuit analysis. There are unresolved mathematical steps and assumptions related to the calculations presented.