SUMMARY
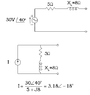
This discussion focuses on solving network nodal voltages and converting voltage sources to current sources using Norton's theorem. Participants clarify that a voltage source in series with a resistor can be transformed into a current source in parallel with the same resistor. The correct current value is derived using the formula I = V/Z, where V is the voltage and Z is the impedance. Additionally, the conversation touches on converting complex numbers from Cartesian to polar form, emphasizing the use of Euler's formula and phasor notation.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Norton's theorem for source transformation
- Familiarity with complex impedance and phasor notation
- Knowledge of Euler's formula for converting between Cartesian and polar forms
- Basic proficiency in using trigonometric functions and calculators for angle conversion
NEXT STEPS
- Study Norton's theorem and its applications in circuit analysis
- Learn about complex impedance and how to perform source transformations
- Explore phasor notation and its significance in AC circuit analysis
- Practice converting complex numbers between Cartesian and polar forms using examples
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineering students, circuit designers, and anyone involved in analyzing and solving electrical networks will benefit from this discussion.