SUMMARY
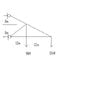
The discussion focuses on calculating the required cross-sectional area of members in a pin-connected truss subjected to loads of 10kN and 35kN, with allowable stresses of 150MPa in tension and 75MPa in compression. To determine the cross-sectional area, one must first calculate the force in each truss member and identify whether each member is in tension or compression. The relationship between stress, force, and area is defined by the formula: Stress = Force/Area. Understanding free body diagrams is essential for visualizing the forces acting on the truss members.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of truss structures and their components
- Knowledge of stress calculations in engineering
- Familiarity with free body diagrams
- Basic principles of mechanics, specifically tension and compression
NEXT STEPS
- Study the method of joints in truss analysis
- Learn about calculating forces in truss members using the method of sections
- Explore the application of allowable stress criteria in structural design
- Review examples of free body diagrams in engineering mechanics
USEFUL FOR
Engineering students, structural engineers, and anyone involved in the analysis and design of truss structures will benefit from this discussion.