- #1
PhysicS FAN
- 26
- 4
- Homework Statement
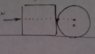
- An object of mass m=2kg rests in a horizontal level with a coeffcient of friction μ=0.5. A cylinder with radius R is placed near the first obect. The mass of cylinder is m=2kg and we know that Ι=1/2mR^2. At a some time instant we start pushing the system with a force of 23N, in such a way that the force passes through the center of the cylinder. What is the acceleration of the system?
Correct Answer: a=2m/s^2
- Relevant Equations
- ΣF=ma, Στ=Ia(angular), T=μmg
For the non-circular object of mass m: From Newtons second law we get that F-N-T=ma where N is the force that the cylinder acts on the object. Replacing numbers: 13-N=2a.
For the cylinder: From Στ=Τa(ang) we get that T'= 1/2ma or T'=a. Where T' is the friction that acts on the cylinder and we assume that its static which means a=a(ang)R.
From ΣF=ma we get N-T'=ma where N' is the reaction of N. N=3a.
Replacing: 13-3a=2a or a=13/5. and if we do the math for the firction we see that the friction for the cylinder is indeed static.
I don't know where I am wrong. Any Help?
For the cylinder: From Στ=Τa(ang) we get that T'= 1/2ma or T'=a. Where T' is the friction that acts on the cylinder and we assume that its static which means a=a(ang)R.
From ΣF=ma we get N-T'=ma where N' is the reaction of N. N=3a.
Replacing: 13-3a=2a or a=13/5. and if we do the math for the firction we see that the friction for the cylinder is indeed static.
I don't know where I am wrong. Any Help?