- #1
reterty
- 29
- 2
Homework Statement
Dear colleagues, my problem is following:
The ball of mass
It is necessary to find the final velocities of the first ball and the center of mass of the second system, considering the impact to be absolutely elastic and occurring along the line through the centers of the balls and the spring.
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
The law of the momentum conservation has form: :
Attachments
-
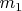 0429e3dd940669f4c728ca27fe91530182.png272 bytes · Views: 551
0429e3dd940669f4c728ca27fe91530182.png272 bytes · Views: 551 -
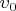 23e0281f80bad171b4adffa1649b3fef82.png259 bytes · Views: 504
23e0281f80bad171b4adffa1649b3fef82.png259 bytes · Views: 504 -
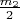 78dab0d04dc1059f0ff1bd20a12558f682.png290 bytes · Views: 576
78dab0d04dc1059f0ff1bd20a12558f682.png290 bytes · Views: 576 -
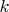 63bb9849783d01d91403bc9a5fea12a282.png247 bytes · Views: 380
63bb9849783d01d91403bc9a5fea12a282.png247 bytes · Views: 380 -
 2f2322dff5bde89c37bcae4116fe20a882.png223 bytes · Views: 363
2f2322dff5bde89c37bcae4116fe20a882.png223 bytes · Views: 363 -
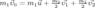 bed2e166f354302d759a83940b7bea7d82.png817 bytes · Views: 361
bed2e166f354302d759a83940b7bea7d82.png817 bytes · Views: 361