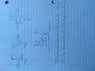Samuelriesterer
- 110
- 0
Problem Statement
Two identical spheres of radius r are placed inside a cylinder of radius R as shown in the diagram below. You are given that R/2 < r < R and that each ball has a weight W. All surfaces are smooth. Show that there is a minimum mass, m, of the cylinder which will allow it to remain upright (for smaller cylinder masses, the cylinder tips over. Show that this mass is given by
m = (2W/g)(1-r/R).
Relative equations:
t = Fr sin theta
I = integral(r^2) dm
Work so far:
See attached picture and document. I have calculated d, the distance from the point of axis to the point of force as:
d = a + R = 2*sqrt(-r(r-2R)) + R
I think I am supposed to find the torque needed to tip the cylinder so I need to find the moment of inertia. But I am really unsure how to begin this problem.
Any help is appreciated.
Thanks!
Two identical spheres of radius r are placed inside a cylinder of radius R as shown in the diagram below. You are given that R/2 < r < R and that each ball has a weight W. All surfaces are smooth. Show that there is a minimum mass, m, of the cylinder which will allow it to remain upright (for smaller cylinder masses, the cylinder tips over. Show that this mass is given by
m = (2W/g)(1-r/R).
Relative equations:
t = Fr sin theta
I = integral(r^2) dm
Work so far:
See attached picture and document. I have calculated d, the distance from the point of axis to the point of force as:
d = a + R = 2*sqrt(-r(r-2R)) + R
I think I am supposed to find the torque needed to tip the cylinder so I need to find the moment of inertia. But I am really unsure how to begin this problem.
Any help is appreciated.
Thanks!