SUMMARY
Umklapp scattering is a critical phenomenon in solid-state physics that involves the interaction of phonons, specifically how their momentum is affected by the periodic structure of a crystal lattice. The discussion highlights that k-vectors outside the first Brillouin zone are equivalent to those within it, emphasizing that k values differing by 2π/a represent the same physical state. The relationship between k values and atomic displacement during lattice vibrations is illustrated through cosine functions, demonstrating how different k values affect the phase of atomic oscillations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of phonon momentum and lattice vibrations
- Familiarity with Brillouin zones and k-vectors
- Knowledge of cosine functions and their graphical representation
- Basic concepts of solid-state physics
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of Umklapp scattering in detail
- Learn about Brillouin zones and their significance in solid-state physics
- Explore the mathematical representation of phonon dispersion relations
- Investigate the role of lattice vibrations in thermal conductivity
USEFUL FOR
Physicists, materials scientists, and students studying solid-state physics, particularly those interested in phonon behavior and crystal lattice dynamics.
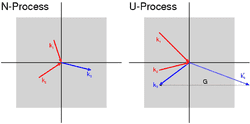 n process on the left, u process on the right
n process on the left, u process on the right