Carmen Wong
- 2
- 0
1. Explain, using the Sauerbrey equation, how the change in the resonance frequency of a quartz crystal can be related to an analyte concentration
2. Sauerbrey equation:
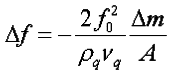
3. I knew Quartz crystal microbalance work according to the change of frequency after mass loaded, and when working in a Newtonian liquid the corresponding frequency shift is
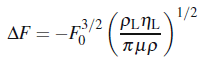 (Kanazawa and Gordon, 1985), whichηL is the liquid viscosity; andμ is the shear modulus.
(Kanazawa and Gordon, 1985), whichηL is the liquid viscosity; andμ is the shear modulus.
But I cannot understand the relation between the change of frequency and the analyte concentration according to the Sauerbrey equation.
thank you for helping
2. Sauerbrey equation:
3. I knew Quartz crystal microbalance work according to the change of frequency after mass loaded, and when working in a Newtonian liquid the corresponding frequency shift is
But I cannot understand the relation between the change of frequency and the analyte concentration according to the Sauerbrey equation.
thank you for helping