Discussion Overview
The discussion revolves around the treatment of surface effects in the van der Waals equation, particularly how different surface areas of containers may influence pressure calculations in gases. Participants explore theoretical implications, experimental observations, and the assumptions underlying the equation.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
- Experimental/applied
Main Points Raised
- One participant questions how surface area is accounted for in the van der Waals equation, suggesting that different container shapes should lead to varying surface effects on pressure.
- Another participant challenges the notion that surface effects are solely due to intermolecular forces, asking for references to support this claim.
- A participant cites Wikipedia to explain that van der Waals assumed a homogeneous fluid density and that surface particles experience a net inward force, which reduces pressure on the walls.
- One participant shares experimental observations from pressure vessels, noting that different internal layouts resulted in different final pressures despite equal initial conditions.
- Another participant argues that the van der Waals equation is independent of surface effects and applies primarily to the interior of a fluid, provided the surface-to-volume ratio is small.
- A participant discusses the implications of non-isothermal conditions in experiments and questions whether interactions with container walls should be considered.
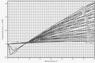
- There is a query about using compressibility factor charts for weakly-interacting gases under specific temperature and pressure conditions.
- Participants express interest in the z-factor charts and seek sources for data to reconstruct these charts.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants do not reach a consensus on how surface effects should be treated in the context of the van der Waals equation. Multiple competing views are presented regarding the influence of surface area, intermolecular forces, and experimental conditions.
Contextual Notes
Some assumptions regarding the homogeneity of the fluid and the nature of interactions between gas molecules and container walls remain unresolved. The discussion also highlights the complexity of applying the van der Waals equation in practical scenarios involving high pressures and dynamic conditions.
Who May Find This Useful
This discussion may be of interest to researchers and practitioners working with gas behavior in confined spaces, particularly in the fields of thermodynamics, chemical engineering, and experimental physics.
 !
!