SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the implications of flipping the inputs of an operational amplifier (op amp) in a circuit. When the inputs are switched, the negative feedback mechanism is disrupted, leading to different circuit behavior. The ideal op-amp assumptions, such as infinite gain and equal input voltages, only hold true under negative feedback conditions. Without this feedback, the circuit behaves more like a comparator, which can yield unexpected output values, particularly under non-ideal conditions.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of operational amplifier (op amp) fundamentals
- Knowledge of feedback mechanisms in electronic circuits
- Familiarity with Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)
- Basic concepts of linear and non-linear circuit analysis
NEXT STEPS
- Study the differences between negative and positive feedback in op amp circuits
- Learn about the Schmidt Trigger circuit and its applications
- Explore the effects of real-world conditions on op amp performance, including noise and power supply variations
- Investigate simulation tools for op amp analysis, such as SPICE or LTspice
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, circuit designers, and students studying analog electronics who seek to deepen their understanding of operational amplifier behavior and feedback systems.
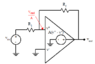
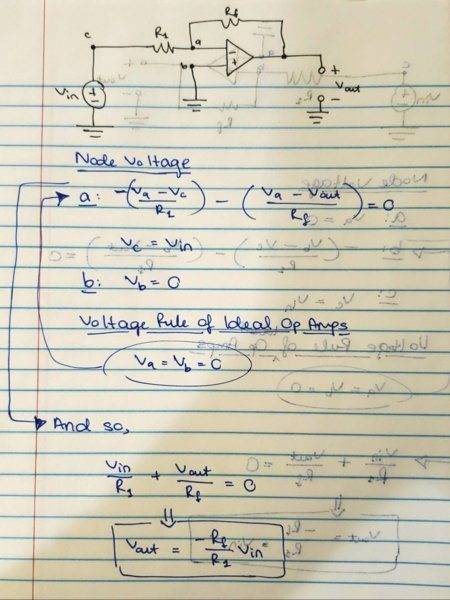 However, when I switch the terminals of the op amp and follow through with the equations, I get the same Vout.
However, when I switch the terminals of the op amp and follow through with the equations, I get the same Vout.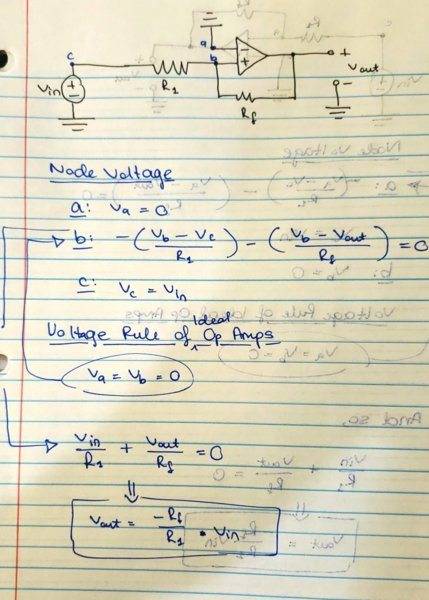 So my question then is what is the difference? I know there is other circuitry involved with the op amp internally, so I guess that's involved but I haven't gotten there yet.
So my question then is what is the difference? I know there is other circuitry involved with the op amp internally, so I guess that's involved but I haven't gotten there yet.