SUMMARY
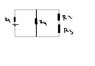
The discussion focuses on calculating the equivalent resistance in a series circuit involving resistors R1, R2, R3, and R4. The correct approach involves recognizing that R2 and R3 are in series, resulting in a combined resistance of 4Ω, which is then in parallel with R4. The final equivalent resistance (Re) is determined using the formula 1/Re = 1/4Ω + 1/2Ω + 1/2Ω, leading to Re = 4Ω/5. Participants emphasize the importance of correctly identifying series and parallel connections to solve the problem accurately.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of series and parallel resistor configurations
- Basic knowledge of Ohm's Law
- Familiarity with calculating equivalent resistance
- Ability to interpret circuit diagrams
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of series and parallel circuits in depth
- Learn how to draw and analyze circuit diagrams
- Explore advanced techniques for calculating equivalent resistance
- Practice problems involving multiple resistors in various configurations
USEFUL FOR
Students studying electricity and physics, electrical engineering learners, and anyone seeking to understand circuit analysis and equivalent resistance calculations.